What is Covert Advertising?
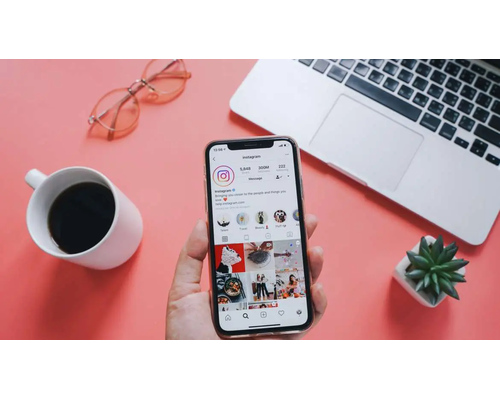
Covert advertising, sometimes known as stealth marketing, is a method by which businesses communicate their offerings without distracting or interrupting the addressee. In Full contrast to standard marketing, which dispatches direct and thereby aggressive messages, stealth advertising is embedded into the content without causing it to stand out or seem bothersome to consumers.
Importance of Covert Advertising
Covert advertising is a way of advertising that can effectively replace “desensitized” traditional marketing tactics. Research by Nielsen discovered that 84 percent of people around the world think that online ads are intrusive, while covert advertising, selling things discreetly, socializes and promotes the products subtly through relatable content and, therefore, is the preferred way.
Case Studies and Examples
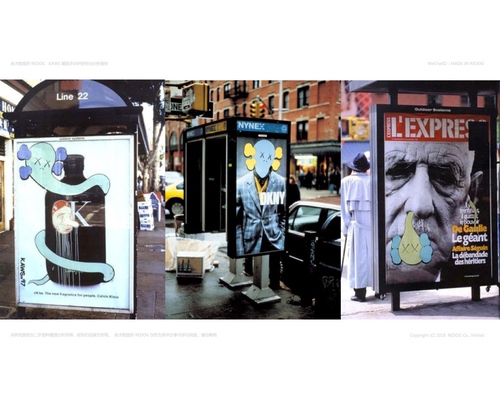
- Product Placement in Film and TV: Product placement in movies and TV series has been happening since the industry-entertainment business was recognized; for example, the Coke intro in every episode of The Friends Show series subtly spreads brand awareness. Let the audience see and make a decision.
- Influencer Endorsements: Influencers are known to incorporate product mentions into their daily posts and stories without them being the main topic. This is one way for them to engage their followers without implicitly promoting the products. The relatedness and trustworthiness of the influencer’s relationship to the product will make a difference.
Frameworks Guiding Covert Advertising
Your customers hold particular beliefs. Business people may get various psychological ideas understood, such as the Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM), which tells how to make people agree by either the deep cognitive process or the superficial cues. Stealth advertising focuses mainly on the peripheral route, assuming previous knowledge and emotions precede logic.
Benefits and Challenges of Covert Advertising

Although the accomplishment of covert advertising lies in producing engagement and relatability, the task of being secret while doing this also brings some challenges.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Consumer Trust: Some people can think of it as less of an intrusion and more of a genuine consumer approach. Thus, they will develop stronger bonds with the brands.
- Increased Recall: When a brand is integrated into captivating stories, readers are more likely to remember it.
Examples:
- One of the well-known YouTube channels describing a specific skincare routine mostly incorporates into practice products endorsed by the creator without the hint that it is an advertisement. Such viral videos create sufficient interest and even convert some viewers to buyers.
Challenges:
- Transparency Issues: Transparency issues can occur in cases where truthfulness is not obtained because consumers do not even know what they are consuming.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Brands that are not transparent about marketing may face public backlash as the public is more likely to act on the word of mouth of their trusted peers or family members who they have a good relationship with or even for what a stranger said who gained their trust -influencers and their followers in particular.
Practical Strategies:
- Balance Authenticity and Disclosure: Companies must carefully distinguish between openness and subtleness; customers must know when a post sponsor is involved.
- Leverage User-Generated Content: Having a loyal fan base to encourage your audience to exchange their stories is the main target of covert advertising while creating a community, yet another way to do this.
Emerging Trends and Implications for Covert Advertising

As consumers become smarter, the landscape of covert advertising is changing. For brands, knowledge of the latest is important for adapting their strategies effectively.
Current Trends:
- Social Media Integration: The new trend is that platforms like TikTok are popular with influencers who create exciting content for brands, combining the individual’s creativity with the topic’s virality to get consumer attention.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Experiences: The ongoing development of AR brands is trial and error. Companies are currently trying to develop virtual products that engage and inform their customers rather than just advertise.
Implications for the Industry:
With changes in gadgetry, so is the art of disguise commercials; advertisers must use the credibility of customers responsibly and respect their privacy in the marketing process. Brands that embrace consumer intelligence are bound to form a strong connection and, therefore, have an edge in a market with numerous competitors. To sum up, covert advertising opens up a new space for companies to connect with their customers more deeply. By understanding the strategies, considering the pros and cons, and looking at cutting-edge techniques, firms can make this landscape manageable and maintain a bond with their customers.
Conclusion
Today’s marketplace is driven by companies striving to establish authentic relations with their audiences through knowledge of covert advertising and the skills to modify such strategies if necessary. Covert advertising, which is the non-intrusive integration of promotional content into entertainment or media, is a great way for the brand to be known and involved in communication with consumers. Determine the probable consequences of the ethics and practical considerations of these actions and thus produce the kind of promotion that speaks to the demographic effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition: Covert advertising subtly integrates promotional material into content to make it more agreeable for the consumer and less noticeable than traditional ads.
- Strategies: Successful covert advertising, which includes product placement, influencer partnerships, and narrative-driven advertising that is sales without being obvious to the target of the advertisement, is non-aggressively successful clandestine advertising.
- Implications: The effectiveness of the employed method might provoke ethical debates about transparency and trust in honesty, with the customer making a moral choice between these two.
- Examples: The best campaigns that use undercover marketing are known to be the ones by Coca-Cola in Hollywood, Nike with their endorsements of athletes, and media streaming companies that show brands in the scenes of the series without disturbing the flow of the stories.
The key to covert advertising involves companies that want to continue attracting new customers in a dynamic media ecosystem while building and sustaining healthy relationships with existing customers.
]]>Key Points:
- Impact on Consumer Behaviour: Advertising significantly influences the marketing of products and services.
- Persuasive Communication Strategies: More strategies will be talked over that capture attention in an attempt to try out sales.
- Ethical Requiring Situations: Responsible practices in advertisements need honest and transparent terms.
Consumers are getting increasingly choosier, demanding brands that interpret themselves along with values. That said, it challenges companies to strategize on ethical aspects of advertising that resonate well with socially aware consumers. By this, more morally driven branding attracts more emotions from consumers. This will lead to brand loyalty and eventually promote profitability.
- Conscious Consumers: Today’s consumers want brands that support their value proposition.
- Emotional: Ethical advertising generates more relationship-building for brands with customers.
- Financial: Companies committed to ethical practices usually experience customer loyalty and increased sales.
Persuasion is the thin line between great art and manipulation. Though persuasive advertising is necessary to help drive sales, it must be used carefully not to tread any lines beyond ethical territories. The list should always include ensuring a strategy does not take advantage of consumer vulnerabilities or distribute false information. The goal should be an enlightening and inspiring marketing campaign rather than a deceptive one that manipulates consumers.
Ad Ethics

Advertising ethics is the morality approach to advertisement creation and distribution. Most of these aspects relate to issues such as truthfulness, fairness,, and respect toward the audiences. Ethical advertisements promote products or services without misleading customers or taking advantage of the vulnerable population.
Key Points:
- Moral Principles: Advertising ethics includes honesty, fairness, and audience respect.
- Enforcement of Responsibility: Advertisers should be mindful of the broader consequences of their advertisements.
- Influence through Regulation: Adherence to codes contributes to developing responsible advertising.
Feeling responsible is the most critical concern of advertisement ethics. It’s not just to the clients but certainly to society that advertisers have been entrusted with a responsibility to understand and take cognizance of the more tremendous implications of their messages and their ramifications on public perception or behavior. As media consumers evolve further, the ethical environment becomes more confusing, challenging advertisers to proactively deal with possible ethical dilemmas that develop out of advertisements.
In addition, the regulatory environment, to a large extent, dictates the ethics of advertising. Agencies and organizations establish norms that will ensure the industry embodies ethical behavior. The advertiser needs to be informed of the general direction of the regulations and strive to adapt to them, yet do more than the bare minimum from the law. By engendering an ethical culture within themselves, the advertisers contribute to how consumers perceive the marketplace; the more trust there is in the market, the easier it is to build consumer confidence.
Necessity of Ethics in Advertising
Building Consumer Confidence

Trust is one of the main parameters behind any healthy business relationship. Ethical advertising builds trust between brands and the consumers. If customers believe the brand to be honest and transparent, then they will want to spend time with that brand and buy it again and again. Conversely, unethical advertising can cause a lot of damage to the brand’s reputation while inviting customer dissatisfaction and loss of loyalty.
Key Take Away:
- Trust Building: Ethical practices lead to repeat purchases or repeat customers.
- Social Media Ripple Effect: The consumers share experiences promptly, making the ethical advertisement force multiply expeditiously.
- Long-Term Investment: Trust built through ethical advertisement may ensure significant returns.
It is an age where, with endless information at their disposal, consumers express their feelings—whether negative or positive- on social media. This time-sensitivity piques the opportunities for responsible, ethical advertisement. The brands that emphasize honesty build positive talk among the customers, as honesty generates conversations naturally. Otherwise, unethical maneuvers can land a brand in a situation of swift backlash; thus, harm can remain for a longer time and extend beyond transactions to the brand experience. Whenever consumers trust that a brand is running ethical affairs, they can easily endorse the brand to other consumers; this makes positive brand equity. Hence, creating trust through ethical advertisement is an investment in the long run, which fetches high returns.
Building Brand Prestige

A sound ethical ground not only builds trust but also strengthens a brand’s reputation in the marketplace. Most importantly, consumers are increasingly drawn to companies that operate on social responsibility and ethics. Ethical advertisements will help companies stand out and attract socially responsible consumers away from their competitors.
Key Take-Aways:
- Differentiation: Ethical advertisement makes a difference in a competitive marketplace.
- Positive Asset: A sound reputation is an asset that will help brands hold out against crises and fluctuations in market conditions.
- Ethical Practice: Leads to higher employee morale and retention.
A good reputation is a valuable asset to a brand. The better the reputation, the easier it is for a company to overcome market conditions and other crises. Brands with a questionable reputation will find it hard to regain consumer trust even when they have cleared their names from any crime. Ethical advertisement is thus necessary to ensure a good reputation for a brand in the long term.
Fair advertising practices lead to higher employee satisfaction and retention rates. Employees would be proud to work for brands that reflect their values. Such an atmosphere at work would be reflected in authentic brand messages, furthering the brand’s esteem in the consumer’s eyes.
Promoting Fair Competition

Ethical advertising promotes fair competition in industries. The reason is that when brands follow the same principles of truthfulness and transparency, a level playing field exists. Unethical practices like false advertising or deceptive marketing would be a blow to competition and thus create an uneven marketplace.
Key Points:
- Level Playing Field: Ethical standards ensure fair competition between brands.
- Encourage Innovation: Genuine value-based differentiation drives ethical practices among brands.
- Adherence to Ethical Standards: Promotes industry credibility through regulatory enforcement.
Competition and fairgrounds support innovation and creativity because brands must create grounds for differentiation based on real value rather than pseudo strategies. Healthy competition may lead to better products and services; hence, consumers’ welfare is incorporated into the effects. Ethical advertising would spur success for individual brands and the health of the market at large.
In addition, there are cases where regulatory agencies demand that different ethical practices to the standards be adopted so that equal competition is received and enjoyed by all. Whatever ethical practice an advertiser adopts ensures that the industry is credible. This joint adoption of ethics establishes consumer confidence and a marketplace where businesses compete on merit and value.
Promoting Social Responsibility

Advertising will influence the attitudes and behaviors of society. Therefore, an advertiser can bring social change by building campaigns based on ethical values. Examples include advertisements on inclusivity, diversity, or environmental sustainability issues that go a long way as consumers are emotionally charged to act.
Key Points:
- Positive Influence: Ethical advertising yields social change and responsibility.
- Identity with Movements: Brands that align with leading causes align with the socially conscious consumer.
- Building Community: This ethical approach towards advertising might bring a sense of belonging and connection with consumers.
Using responsible social advertising, brands can have their voice in initiating those conversations about issues that need to be discussed and align themselves with movements that call for change. Sustainability would be an excellent example of that—it creates a brand image and endangers consumers’ consumption choices. It creates a domino effect where people are inspired enough to make that change in their lives, too.
Socially responsible advertising also creates a group feeling among consumers. Brands that engage with social causes express concern for their audience’s values and concerns, growing the emotional bond between the brand and its customers. This association will increase loyalty and advocacy as consumers are empowered to support brands sharing their values.
Critical Ethical Issues in Advertising
False and Misleading Claims

False and misleading ads are among the most significant ethical issues advertising faces. There may be the exaggeration of the benefits of a product made by an advertiser, critical information may not be added in the ads, or ambiguous language might be used against consumers to mislead them. Such practices are unethical and have legal repercussions under the law of consumer protection.
Key Takeaways:
- Legal Consequences: False and misleading advertisements may lead to potential legal action against it and also give space for branding its reputation.
- Consumer Awareness: The Scourge of Social Media Increases Scrutiny of Advertising Claims.
- Cultural Shift: Brands Must Champion Truthfulness to Protect Industry Integrity.
The invention of social media has made it easier for consumers to vocalize their opinions; therefore, the scrutiny of advertisements is higher than in previous years. Misleading brand practices are mainly exposed by consumers, which destroys their reputations. In addition, regulatory agencies are becoming astute in enforcing stiffer punishments on brands that mislead consumers.
To address this issue, there has to be a cultural shift in the organization, establishing truth-telling as a norm when advertising to the public. Advertisers must develop robust verification processes to prove every advertisement claims one big lie. This would ensure consumer security, simultaneously strengthening the profession of advertising.
]]>In the dynamic realm of marketing, the principles that guide ethical advertising are indispensable. The source forecasts that, in 2023, the marketing spending on offline channels in the United States will amount to 202 billion U.S. dollars. At the heart of this crucial facet lies the inquiry: “What is advertising ethics?”
This question beckons us to explore the moral compass that should underpin every promotional endeavor. Advertising ethics involves navigating the delicate balance between creativity, persuasion, and responsibility. It delves into the integrity of messaging, ensuring truthfulness, and the fair treatment of consumers.
Moreover, the question of what is advertising ethics encompasses the broader concept of a code of ethics for advertisements, delineating the boundaries within which advertisers should operate. Understanding the different ethics of advertising becomes imperative in a landscape where societal values continually evolve.
From the promotion of diversity and inclusivity to the avoidance of deceptive tactics, what is advertising ethics is multifaceted. This exploration seeks to unravel the layers of ethical advertising, providing insights into the conscientious practices that uphold the integrity of the industry.
What is Advertising Ethics And Why is It So Important?
Advertising ethics are very important for several reasons. First of all, it promotes consumer and advertiser trust. Customers are more likely to have favorable opinions of brands and make wise purchasing decisions when they believe that commercials are honest, open, and kind.
Second, moral advertising enhances a business’s or industry’s reputation in general. Prioritizing ethical behavior helps advertisers draw in devoted clients as well as credibility and public favor. On the other hand, unethical advertising can harm a company’s reputation and have unfavourable long-term effects.
By using ethical advertising, you can make sure that you aren’t offending anyone. When delivering adverts, the advertiser should adhere to a code of conduct.
Adhering to societal norms and refraining from deception are hallmarks of ethical advertising. Advertising ethics also contribute to the development of a company’s and brand’s reputation.
Ethical Advertising VS Unethical Advertising: What is Code of Ethics for Advertisement

According to the definition of what is advertising ethics, which we previously discussed, it is a collection of moral guidelines that establish limits between the seller and the customer. In light of this, we can state that modern businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to broaden their customer base and boost revenue.
And since businesses are constantly searching for innovative ways to promote their goods and services, this could result in some unethical advertising techniques.
On the other hand, truthfulness in advertising relates to the goods or services that a company provides. Advertising that tries to conceal a product’s shortcomings by withholding information about a service is considered unethical.
Advertising that misrepresents a good or service in any manner or uses subliminal messaging to further a covert goal is considered unethical. In order to enhance sales, this type of advertising manipulates or persuades the consumer to purchase the good or service.
When you are exploring the what is code of ethics for advertisement, your advertising should have transparent goals and no ulterior motives, regardless of whether you are using an in-house marketing team or an external marketing agency.
So, let us learn about the 7 principles that every ethical advertisement should follow:
What are the Different Ethics of Advertising: The 7 Principles

The basis of what is advertising ethics is based on seven principles that outline the appropriate channels of contact between vendors and consumers. These tenets provide a framework for thought, detailing the moral considerations that companies and marketers ought to build into their operations. Let’s take a closer look at each of these advertising ethics guidelines.
1. Principle 1
Advertising, public relations, and marketing for any business should all share a common objective of truth and high ethical standards toward the customers.
Consumers regularly place a high value on advertising that is honest and ethically produced, according to research. Consumer opinion is positively impacted when companies maintain ethical standards and speak openly. Since trust plays a major role in consumer decision-making in this day and age, businesses that want to establish and sustain good relationships with their target audience must place a high value on honesty and integrity.
2. Principle 2
As a business owner, your marketing campaigns should have an obligation to exercise the highest personal ethics in the creation of commercial information for consumers.
The emphasis on marketing campaigns highlights the strategic value of moral behaviour in advertising, requiring truthfulness, integrity, and openness. The principle advocates for the seamless integration of ethical ideals into both personal and commercial decision-making, going beyond a simple professional expectation by placing the requirement firmly centered on personal ethics.
It quietly recognises the effect on brand image, presenting ethical marketing as both a moral requirement and a calculated decision that is necessary to build long-lasting relationships with customers and trust.
3. Principle 3
Advertisers and marketers should clearly differentiate between advertising and news and editorial content, both offline and online.
Concerns regarding consumer deceit and unethical treatment are raised by this tendency. The reference to consumers being deceived highlights the detrimental effects that could occur for people who struggle to tell the difference between legitimate editorial content and promotional communications.
The statement asks for a coordinated effort by the industry to solve this problem and reduce the possibility of customer misunderstanding and mistrust. The need of clearly separating sponsored advertisements from real news material is emphasised. In addition to being viewed as a precaution against consumer confusion, this division is also presented as a moral requirement to uphold honesty and transparency in the communication environment.
4. Principle 4
In marketing campaigns, advertisers and marketers should disclose all the material conditions including the payment or receipt of free products.
The statement highlights how important it is for advertisers to be transparent about the nature of their connection with businesses and bloggers. Advertisers are specifically advised to clarify whether bloggers are endorsing products out of genuine personal opinion or whether they are being paid by a company to do so.
Furthermore, the declaration promotes total openness concerning the integrity of remarks on social networking sites like Facebook and Twitter. This request for disclosure emphasises how crucial it is to preserve openness in the digital sphere, guarantee that users can make knowledgeable decisions about the content they come across and uphold the moral standards that are anticipated in modern marketing and advertising campaigns.
5. Principle 5
Through advertising, advertisers should pay extra care to the customers that these advertisements are for, to avoid any misunderstanding and misleading.
Advertisers must use more caution and sensitivity in their communication techniques since they are aware of how susceptible these audiences are. The statement also emphasises the value of exercising judgment, especially when it comes to the kind of good or service being advertised. Advertisers are advised to use even more caution when it comes to prescription medications and alcohol, as there are major dangers and repercussions involved.
This means that judgments about advertising should be based primarily on ethical concerns, with an emphasis on preventing harm, disinformation, and the exploitation of vulnerable populations. The statement essentially promotes the use of a careful and responsible approach in advertising, particularly when targeting groups who might be more receptive to the effects of marketing messaging.
6. Principle 6
It is completely unethical for an advertiser to use a customer’s personal privacy in marketing communications.
Customers are voicing growing concerns about possible privacy violations as marketers use more sophisticated methods to customise ads based on unique internet activity. Marketing and media trade associations are responding proactively to government directives and consumer concerns.
To be more precise, they are starting an online self-regulatory program to give users more choices over how their internet-watching data is collected and used. By giving people control over the collection and use of their personal data online, this initiative aims to allay privacy concerns. It is part of an industry-wide effort to strike a balance between the need to protect consumer privacy and efficient advertising tactics.
7. Principle 7
Advertisers should privately discuss potential ethical concerns, and members of the team creating ads should be given permission to express their ethical concerns.
Advertisers looking for ethical standards and regulatory guidelines should consult reputable organisations such as the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), Better Business Bureau (BBB), and Federal Trade Commission (FTC). These organizations are essential in monitoring and controlling many facets of advertising to guarantee impartiality, openness, and adherence to laws.
The statement also highlights the National Advertising Review Council (NARC), a self-regulatory initiative started by the industry. NARC stands out for its thorough coverage, which covers moral issues in advertising for both adults and children. This highlights the advertising industry’s dedication to upholding moral standards through self-regulation, exhibiting a proactive strategy for preserving customer trust and fulfilling legal requirements.
Winding It Up

Advertisers themselves gain from ethical advertising as well as consumers, who gain from correct information and the ability to make wise judgements. In addition to building a strong brand and gaining devoted customers, advertisers that put ethics first can also improve the industry’s standing.
Considering all that has been said thus far, advertisers ought to begin assuming accountability for self-regulating their commercials by:
- Create self-regulatory standards for their businesses that cover moral principles, the truth, decency, and the law.
- Continue monitoring the activity and take down any advertising that don’t match the codes.
- Notify customers of the company’s self-regulation codes.
- Keep an eye out for customer complaints regarding product advertisements.
- Ensure that the system and the firm are transparent.
When the aforementioned suggestions are put into practise, they will lead to:
- Holding the business accountable for all of its actions
- Will lessen the likelihood of being called out by an oversight organisation.
- Will aid in gaining the trust of the public and inspire confidence in the business and its offerings.
In summary, advertising ethics are essential to forming the advertising environment and preserving a positive consumer-advertiser connection. Advertisers can establish beneficial cultural norms, encourage openness, and inspire trust by upholding ethical principles. In the field of advertising, the value of integrity, openness, decency, and social responsibility cannot be emphasised.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the meaning of advertising ethics?
The moral guidelines that direct a company’s interactions with members of its target audience are known as advertising ethics. A supplier of goods or services and a prospective customer can communicate in a number of ways, as outlined by a set of established rules in advertising.
2. What are the advertising ethics in India?
The goal of advertising should be to win people over with the qualities of the products or services being promoted. Negative remarks and direct comparisons with rival products or companies are strictly prohibited.
3. What is advertising ethics of sales?
A set of actions that guarantee that each lead, prospect, and customer is handled with dignity, equity, truthfulness, and integrity is known as sales ethics. In other words, as a marketer or salesperson, you prioritise the customers you serve. Rather than pushing your ideology on others, you show respect for their decisions and viewpoints.
4. What is advertising ethics issues?
False advertising. When a business exaggerates or embellishes the advantages of its goods and services, it is engaging in false advertising. Presenting negative stereotypes. Mishandling client information or inappropriate promotional material.
]]>Ready to talk with a marketing expert?
Get in Touch
Rukmini Knowledge Park, Kattigenahalli, SH 104, Srinivasa Nagar, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560064
+91-990 247 8800
contact@gingermediagroup.com
Popular in Television Advertising
Udaya TV AdvertisingSun TV AdvertisingStar Plus AdvertisingTV 9 AdvertisingZee TV AdvertisingNDTV India AdvertisingColors TV AdvertisingPopular in Airport Advertising
Spice Jet AdvertisingMumbai Airport AdvertisingDelhi Airport AdvertisingEmirites AdvertisingIndiGo Airlines Domestic India AdvertisingPopular in Newspaper Advertising
Deccan Herald AdvertisingPrajavani AdvertisingThe Hindu AdvertisingEconomic Times AdvertisingDainik Jagran AdvertisingHindustan Times AdvertisingPopular in Magazine Advertising
Forbes AdvertisingCosmopolitan AdvertisingBusiness World AdvertisingVogue Magazine AdvertisingPopular in Sports Advertising
IPL AdvertisingPopular in Outdoor Advertising
Billboard AdvertisingBus Shelter AdvertisingMetro Pillar AdvertisingUnipole Advertising© Ginger Media Group 2025. All Rights Reserved.
