The new marketing landscape includes many means to ensure that the targeted audience is reached. Among these methods is magazine advertising, which has been utilised as a powerful means by brands to achieve targeted audiences. However, magazines use diverse types of ads. Thus, marketers need to understand the various ad types, their purposes, functions, and real-world applications. This guide will explore each ad type, enabling businesses to employ whatever knowledge they obtain to improve their advertising strategies.
Overview of Different Forms of Magazine Advertisements
Magazine marketing is a tremendous method through which companies can convey their messages. The form of advertisement will determine all the differences in visibility and interaction between the brands and the target market. In that respect, there are a few things to look out for:
- Multi-Formats: From full-page spreads to classified lists, magazine ads provide each business’s unique marketing needs.
- Reaching the Target Possibility Audience: Different ad types can target different demographics, so marketers have to know their possibilities.
- Resource Budget: Knowing which ad type will benefit them in what way allows decision-makers to budget their resources wisely.
Why the Knowledge of Various Kinds of Magazine Ads Is Important

Knowing various kinds of magazine ads empowers marketers and business leaders to create efficient advertisement strategies. The following is why knowledge in this regard is essential:
- Sophisticated Strategy: There are full-page and partial ad types for branding and lead generation, among other marketing goals. Depending on their preferences and consumption behaviour, ads can interest their consumers.
- A knowledgeable selection of an appropriate ad can deploy resources more efficiently and increase the return on investment.
Types of Magazine Ads: Purpose, Role, and Application
1. Full-Page Advertisements

- Definition and Objective:
Full-page ads take the whole page of a magazine, meaning maximum visualisation. Since they are done strategically, one gets caught immediately to attract the reader’s attention through bold imagery, great headlines, and tremendous content. Due to their size, they help brands convey detailed information to convey a powerful message. - The most effective way these ads can successfully deliver comprehensive messages or brand stories to target audiences. These can be used to unveil a new product, announce an event of great importance, or launch a marketing campaign. The expansive space allowed for creative freedom, enabling brands to articulate their narratives using vivid visuals and engaging texts.
- Real-World Application:
A luxury car manufacturer with its latest model can run an open-page advertisement in a glossy lifestyle magazine. The two-pager, by way of analogy, would be equivalent to using glamorous pictures of the car in scenic locales, paired with compelling copy centred on excellent technology and performance, to reach affluent consumers with the message to help them become brand lovers.
2. Half Page Ads

- What is a half-page ad? What is its purpose?
Half-page advertisements take up half the magazine’s page; therefore, there is a balance between visibility and costs. This is the right size for an ad to say whatever needs to be told without putting too much strain on the reader’s eye or budget. - Purpose:
Advertisements are meant to convey particular messages fairly succinctly. These may include promotions, special events, or product launches. Because of goals, this means that this advertisement can offer flexibility. - Practical Application:
A fashion retailer may use half-page advertising within a lifestyle magazine to feature its seasonal collection. The advertisement may be highly graphic, exhibiting the prevailing trends and a special discount valid only for a certain period of time. Such a form is markedly effective for catching the attention of the audience and putting them immediately into consumer action, such as visiting a store or shopping.
3. Quarter-Page Ads

- Definition and Purpose:
Quarter-page ads take up only a small section of the magazine page, making them cheaper yet effective in communicating your message. They are also short, but they catch the reader’s attention. - Application:
Local businesses can use quarter-page ads to promote something or an event. They serve with the delivery of the message in due time, thus ideal for time-to-time offers or announcements about events happening in the community. - Realistic Usage:
A tiny coffee shop would place a quarter-page ad for its latest seasonal latte in the community magazine. The ad can appeal to the aesthetics of the drink by publishing some very attractive images and might have a great tagline; if the shop offers a discount, that should also go up. That is how a business engages its community through advertising while driving foot traffic into the shop.
4. Advertorials

- Definition and Purpose:
Advertorials are specially created ads written in the style of an editorial to blend informative content with merely promotional content. This format enables brands to reach readers more meaningfully by incorporating value while subtly marketing their products or services. - Usage:
Advertorials are primarily used to inform and engage readers through a blend of informative content and promotion. Therefore, in their narrative form, a brand can build trust and credibility about what it’s offering. - Real-Life Use Case:
A skincare company would publish an advertorial in a health and wellness magazine discussing the benefits of using organic skincare products. The article would cover topics like organic natural skin care regimes but without overtly focusing on them and using the names of the company’s products within the text. Thus, it would educate the readers and gently push them towards considering the brand for their skin care needs.
5. Sponsored Content
What Is It?
It is sometimes called paid or branded content and must be labelled.
Sponsored content is a valuable information source or storytelling subtly intertwined with a brand message. Unlike traditional ads, this format focuses on the relevance and engagement value of the material presented to the reader.
- Function:
Sponsored content aligns readers’ interests with relevant topics while advancing the product or service being pushed. It gives brands the chance to be thought leaders and to create an aura of truthfulness. - Real-World Application:
For example, a financial services company can establish content under the category “Smart Investing Tips for Millennials,” which gives the reader a practical finance tip while subtly tucking the services inside the article. This way, the brand is more effective in connecting to a much younger crowd, building credibility, and urging the readers to follow through on their offerings.
6. Classified Ads

- Definition and Purpose:
Classified ads are text-based small adverts grouped into categories such as jobs, real estate, or personal services. Compared to other means of advertising, classified ads are relatively cheap and provide businesses and individuals with an easy way to reach targeted customers. - Purpose:
The basic function of classified ads is to connect buyers with sellers through brief information. Most of the adverts contain grouped contact data as well as short descriptions that enable the interested party to reach the adverts. - A small business can advertise a classified ad in a community magazine to list job openings and even briefly describe the position. The company can also list its contact information. This simple method makes it easier for businesses to reach their community and attract potential applicants.
7. Back Page Ads
- Definition and Purpose:
Back-page ads are placed on the rear page of the magazine, marked with high visibility and prominence. They are mostly used for high-budget campaigns and premium brands to ensure maximum visibility of the ad. - Purpose:
They are meant to catch the eye of the reader, as they are placed at the highest place. They are often used in brand launching campaigns, especially in special promotions or the release of significant announcements with which to leave a long-term impact. - Real World Example:
A blockbuster movie release can be advertised on the back page of an entertainment magazine, creating suspense among its spectators for when it will hit the theatres. The ad can include very dramatic scenes from the movie, a short, enticing slogan, and an invitation to readers to go watch it. This kind of ad receives maximum exposure and is sure to be remembered by potential viewers.
History of Magazines Used in Advertising

This is an aspect that business people also need to focus on.
- Engagement by Ad Type
- There are different types of ads which are suited to different demos and interests.
- Knowledge about various types of ads helps brands to ensure that their communication is targeted correctly.
- Branding Position
- Ads in magazines help develop images for brands.
- Differing levels of engagement across the various ad types influence consumer perception.
- Cost Effective
- Knowledge about ad types will help develop an efficient budget.
- Proper choice of ad type leads to better returns on investment.
- Creative Ideas
- Every ad type provides different opportunities to be creative.
- Engaging visuals helps to create brand recall and persuasion.
- Ability to Track and Measure
- There are various kinds of advertisements with numerous tracking options.
- Measuring engagement aids in guiding future advertising directions.
- Long-Term Success in Consumer Relationships
- Advertising in magazines holds more credibility than internet ads.
- Success in the type of ad used leads to long-term relationships with consumers.
Final Thoughts
Understanding types of magazine ads and their configuration translates to the appropriate usage of the configurations to aid in business growth. Summary of main points covered:
- Reach and Engagement: The choice of ad type can better relate to the target population, thereby boosting engagement.
- Brand Positioning: All forms of advertising work toward building a brand image in the consumer’s mind.
- Cost Efficiency: Different types of ads have cost implications. The budget can only be optimal. Making appropriate choices can only optimize the budget. Unique kinds of ads allow the value proposition to be communicated uniquely.
- Tracking/Measurement: Understood ad types can be used to aid in determining strategies’ effectiveness.
- Long-Term Consumer Relationships: Magazine ads that work build credibility and induce customer loyalty over the long term.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct forms of magazine adverts is necessary for a business to maximise the potential of unutilised print media. Once the appropriate advert type has been selected, the marketing objectives will be achieved, the business’s advantage will stand out in a highly competitive marketplace, and growth will ensue.
Key Aspects of TRP:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: TRP provides businesses with vital information that aids them in formulating decisions, such as the best choice of media buying and advertising spots.
- Cost Efficiency: By identifying popular programs and their viewer demographics, firms can identify cost-saving aspects and efficiently utilize their advertising budgets.
- Improved Customer Focus: TRP ensures that advertising, an important part of the value chain, is aligned with customer value; therefore, the organization can prioritize the campaigns that bring the best incremental results to brand building.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly assessing TRP data is an effective tool for businesses as it requires them to modify their strategies. By doing so, they improve their understanding of the clients and thus improve their content delivery.
- Strategic Planning: TRP allows better forecasting and strategic decision-making by showing the main topics of viewer trends, which is why they are in higher demand& that is the way to capture and retain subscribers.
This blog post will examine TRP principles, discuss their relevance in modern business practice, and show how companies can use TRP to communicate better with their audience. Let’s explore useful tips and show you how to integrate TRP into your business strategy!
What is TRP (Television Rating Point)?

The Television Rating Point (TRP) is an index of a television program’s popularity. It gauges a program’s viewership and provides data and metrics of viewer engagement. By discovering audiences’ viewing frequency and preferences, companies can benefit from using this knowledge to make targeted advertising, content creation, and programming decisions, thus optimizing efficacy and income.
Key Components of TRP
1. Audience Measurement: On the one hand, it is about identifying the viewer’s age, sex, and geographic location and knowing who watches what is of the utmost importance for the advertising industry and TV channels, as it allows them to better target content and ads to particular audience segments.
2. Rating Calculation: TRP is a figure arrived at after a program’s audience numbers are measured and its potential total is established. This quantitative technique enables networks to assess a series’ attractiveness and determine the best schedule and ad rates.
3. Viewer Engagement: Apart from the factor of the viewer’s number, interaction with the viewers and comprehension of the way they react to the content are the key elements of the process. It encompasses the audience’s opinions, online interactions with different platforms, and views. Together, these aspects represent the improvement of the stability of TRP metrics.
Benefits of TRP

- Improved Decision-Making: TRP enables TV stations and advertisers to make choices that are, in turn, deeply rooted in statistics. With a detailed idea, the TV network can program its popular shows during peak viewership times, thereby increasing the possibility of the ads’ higher market value.
- Cost Efficiency: Being able to suss out the TRP can be a game-changer in the profits accrued from marketing and advertising. The advertisers can brief names of the programs with higher ratings that help their marketing budget, which is spent on platforms with a broader reach to which they are getting better returns on investment.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Truthful information based on TRP findings involves partnerships between TV stations and advertisers. This, in turn, leads to the open discussion of target segments and retrieval tactics, and therefore, shared campaigns representing the audience are born.
Core Principles of TRP
- Focus on Activities: Knowing the patterns in which people watch television is key to understanding the activities that could influence the program’s popularity. By doing this, broadcasters can understand the needs of their audience and cater to the programs by giving their viewers more control over what they watch.
- Link Activities to Costs: There is a direct correlation between the audience’s activities and advertising costs. The higher show ratings that attract the most viewers can be why a TV station can set higher rates for ads, so advertisers may have to change their pricing policies regarding the rating ranges.
- Continuous Improvement: The television industry is hectic, and nothing has changed. Comprehending TRP trends is a typical KPI among TV networks and marketing corporations, as they always change according to the client’s needs.
Steps to Implement TRP Analysis
- Analyze Current Activities: For this purpose, companies must start by reviewing their audience size and understanding how their programs are working. This will lay the groundwork for the future programming decision-makers will develop to grab their audience’s attention and keep it led.
- Establish Cost Drivers: Discovering which media cost more but are also the most viewed, such as VODs and video via TV networks, is also influential, as ContentDeric, Visyon, and BCN content distribution, for instance. Organizations can thus optimize their business strategies.
- Implement Performance Metrics: Measuring and managing performance via TRP ratings will help companies determine their strengths and weaknesses, develop their best strategies, and modify them if necessary.
- Engage Employees: Including people responsible for all process phases, from contributing to the content to advertising, is a pivotal stage since their knowledge can provide new ways of thinking to create content and different marketing styles.
- Leverage Technology: Scientific signal processing is an equipment-based technology that would enable TV broadcasters to give instant feedback to program providers, allowing them to adjust content accordingly. The agency also suggested the benefits of using such technology in other mass media, such as newspapers and composite videos.
Real-world Examples of TRP
- Example 1: STAR TV Network The STAR TV network recognized that the audience wanted to watch specific shows most of the time by using expensive TRP analytics. Consequently, the network launched the prime-time series that earned ratings exceeding a million views during its debut week. The series was able.
- Example 2: NBC’s “This Is Us” The network took note of the viewer interest in the program and held the promotion of “This Is Us” during sports events to increase the number of viewers. In this sense, the mirror image of confirming the high TRP became the breaking sales record of the TV program.
- Example 3: HBO’s “Game of Thrones” HBO might have been aware of the interests of the show’s fanbase via TRP data so that they could organize the release of promos and airtime accordingly for the show. This led to the huge success of the premiere and the staggering number of subscriptions the service got.
In the final analysis, mastering the TRP through a proper study of the numbers and then enlisting a population-based sample could result in low statistical power. However, the content strategy could be future-proof because organizations will use content strategies to optimize profit to meet the audience’s needs. Also, companies will understand The Equation and how to apply it.
- Compiled Data: Briefly, TRP is a benchmark for quality for companies whose main objective is to become more familiar with their customers and accurately determine their watching patterns. Firms may become more efficient and make better decisions by understanding consumer preferences, using advertising resources more accurately, and through a content strategy that aims at continuous improvement. Company executives predicting and meeting customers’ needs and desires via TRP will have a very good management practice, which they develop by containing the right elements. You can use TRP-based practices in your business and get the following:
- High-quality audience data to guide programming and advertising decisions.
- Logical spending by approaching the right demographic at the right time.
- A better competitive position by implementing data-driven content strategies. Empower yourself now and employ TRP all over your business to turn your organization into a new page. Today, we are more willing to engage with you than ever before. Make sure you listen to them and act accordingly.
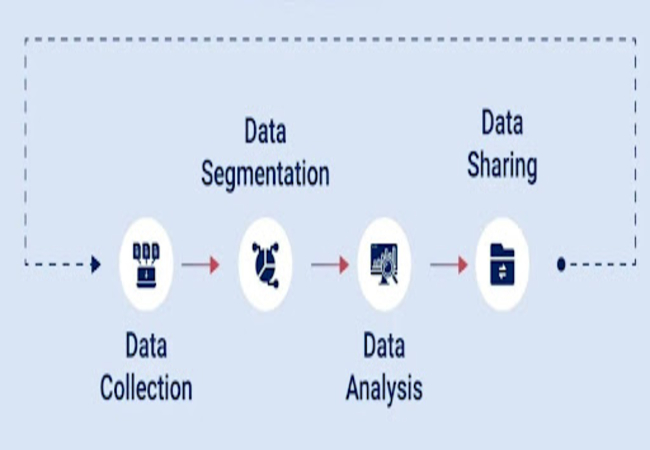
Data management platforms have transformed into an essential tool for organizations looking to leverage their digital marketing capabilities in today’s competitive playground. This innovative concept includes the following:
- Data collection: Collecting data from various sources.
- Data integration: Merging different kinds of data to analyze.
- Data analysis: Deriving insights into targeted campaigns.
Due to an increasing demand for customised marketing strategies, DMP would significantly impact the marketing output of the organization and its interaction with customers.
What DMP Can Do

- Better Decision Making:
DMP provides precious insights into what makes marketing more feasible. That way, marketers will be able to support any informed decision they make. - Cost Effectiveness:
It allows an organization to manage resources efficiently by identifying areas that can bring about savings and minimize unnecessary spending on any marketing budget.
DMP supports the marketing activities to be aligned with customers’ preferences and behaviors, implying an insistence on doing things in a manner that gives the most returns. - Continuous Improvement:
The platform ensures continuous review and approach change to campaigns to ensure campaign relevance and effectiveness. - Strategic Planning:
DMP facilitates better forecasting and long-term decision-making such that marketers can provide a good answer to what is going to happen eventually and design accordingly.
In this blog, we’ll learn about the principles of DMP, the significance of data management platforms in contemporary business practices, and how organizations can tap into it for enhanced marketing effectiveness. Let’s join you in this revelation and discover all the insights and actionable steps to implement DMP into your marketing campaign.
What is a DMP (Data Management Platform)?
DMP, or Data Management Platform, is that technology and software platform which gathers data from disparate sources, manages it, and then analyzes them. Organizations can identify and organize the user’s data to benefit them through these engagements:
- Develop Targeted Advertising Strategies:
Benefit with greater user engagement through insights. - Enhance Marketing Effectiveness:
Use more personalized and result-oriented campaigns.
A DMP empowers marketers to connect with the insights of consumer behavior for more personalized and effective advertising campaigns.
Key Elements of DMP
- Data Collection:
The main aspect of a DMP is data aggregation on first-party, second-party, and third-party data. The rest of the analysis and targeting are based on this foundational element. - Data Segmentation:
Data segmentation refers to the process of classifying collected data according to defined characteristics, behaviors, and demographics to pinpoint specific audience groups.
Data segmentation enhances the overall efficiency of marketing campaigns. - Data Integration:
Data integration is the process of combining data from various disparate platforms and channels to ensure all available data is at one place. This ability has made the implementation of DMP more robust and has also simplified marketing processes while also ensuring campaigns are uniform.
Advantages of DMP
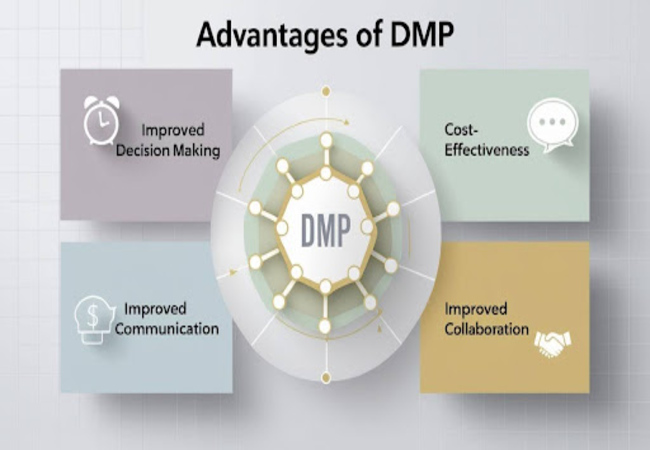
- Improved Decision Making:
DMP may assist in improved decision making since it offers a completely comprehensive view of consumer behavior and preference.
For example, a fashion retailer can adjust its inventory and marketing campaigns that are connected with the purchasing patterns of its customers if it deems after analysis through help of their DMP, that they require such adjustments. - Cost-Effectiveness:
Use of DMP helps in cost efficiency as it enables organizations to derive better returns on advertising spend.
By targeting effectively narrow audiences, businesses can reduce waste ad spend on unlikely to convert the audience. - Improved Communication and Collaboration:
DMP encourages better communication and collaboration with marketing teams.
Access to central data allows teamwork to effectively focus on ensuring each campaign is aligned as well as data-driven.
Principles of DMP
- Activity Focus:
A DMP also should have a clear understanding of what the objective of customer interaction is and what actually drives that activity.
Marketers can adjust their efforts to where they can most maximize interaction by analyzing interactions at every step of the customer journey. - Link Activities to Costs:
Providing a clear relationship between marketing activities and associated costs allows organizations to improve resource allocations.
This way, truly impactful strategies get all the budget they need. - Ongoing Improvement:
The market strategy demands a great extent of constant monitoring and evaluation that, over time, can improve.
DMP always promotes the culture of continuous improvement and is enabled by the realization of data insights into agile marketing tactics.
How to Implement DMP

- Study Current Activities:
The companies have to understand what the marketing and data processes are through an assessment.
Having them functionably integrated, knowledge of current sources of data and interactions by the consumers is always important. - Determine Cost Drivers:
Determining the factors affecting the cost of advertisements helps the business in properly allocating its budget.
Account for engagement levels and channel performance. - Roll Out Performance Metrics:
Setting up as well as monitoring performance metrics helps in benchmarking campaigns’ effectiveness.
Conversion rates, customer acquisition cost, and return on ad spend are KPIs that clearly point out the campaign performance. - Involve Employees:
Involving employees of different departments in the DMP rollout process goes a long way in generating buy-ins and subsequently leading to better strategic alignment.
Training and collaboration are bound to ensure that all the members in the organization learn the value of insights from data. - Technology is Leverage:
State-of-the-art technology and a variety of tools can add huge value to the usage of a DMP.
There exist various platforms that can integrate, analyze, and segment data, thus speeding up the process.
Real-life Examples of DMP
Example 1: The Home Depot

Utilized a DMP in assessing customer behavior both online and at the stores. With their emphasis on data-driven targeted advertising, demographically based on user data and purchasing behaviors, they were able to increase their return on investment by 20%.
Example 2: Procter & Gamble

Embraced DMP to enhance its digital marketing. Data aggregation and analysis of consumer engagement enabled it to calibrate such campaigns that yielded higher retention rates among its customers.
Example 3: Audi

Took a DMP to understand its customers’ journey better. Using the insights they learned, they adjusted their ad strategies. They saw a substantial increase in test drive bookings and sales.
Conclusion: The Role of DMPs for Advertisement
In conclusion, understanding DMP is an approach that is very valuable for organizations that want to improve their advertising strategy and customer interaction. Through gaining a deep understanding of data integration, audience segmentation, and analytics, the company can learn to:
- Relevant Resource Utilization:
Channel resources towards ROI-generating activities. - Marketing Tune:
Fine-tune campaigns in line with information provided by the data and reports. - Continuous Improvement:
Periodically review and update the marketing strategy.
This will free tremendous potential in the workings of business operation processes and their decision-making approach. The more the business would experience market pressure and competition, the more imperative DMP investment would prove to be as a base of successful managerial practices.
- Improved Targeting:
Target the right audience with the right precision to enhance the conversion rates and ROI on campaigns. - Data-Driven Insights:
Make good marketing decisions through robust analytics and the customer behavior data that gives even more impactful campaigns. - Streamlined Resource Allocation:
Optimize the marketing budget with a clear understanding of which strategies work best, helping to identify where to focus efforts to achieve maximum results.
This is the perfect time to embrace Data Management Platforms and experience what it can do for your company. Take the first step today toward optimized advertising strategies and more engagement with customers.
Final Thoughts
In simple words, there is a necessity to understand the distinct forms of magazine adverts for a business to be able to utilize the print media to its ultimate potential. Once the appropriate advert type has been selected, then the marketing objectives will be achieved, their advantage will stand out in a highly competitive marketplace and growth will be ensured.
]]>- Strategic Communication: Advertising is not about conveying a message but rather creating a story that gives the user power.
- Emotional Engagement: Advertising alone can be an effective device for emotional engagement between a brand and a consumer.
- Long-term Impact: Advertising is not about short-term sales; it is a vehicle for building brand identity and loyalty over the long haul.
As we examine this topic, it becomes clear that advertising goes beyond a message; it is a multidimensional approach designed to communicate value and create lasting ties.
Functions of Advertising
1. Building Brand Awareness

Brand awareness is always at the root of a successful marketing plan. Without that, even the greatest products and services can remain in obscurity. It is through advertising that a brand becomes visible and therefore acknowledged by its target audience. Here are three must points regarding brand awareness:
- Target Audience Identification:
Identification of the target group based on demography, interests, and behaviour is equally significant. To achieve this, detailed market research, surveys, and data analysis about the consumer are essential. Using tools like Google Analytics and insights from social media, brands can obtain valuable information related to customers’ preferences and online behaviour. - Compelling Messaging:
A compelling message that communicates with the audience must be created once the target audience is defined. It needs to indicate how the USPs of the brand have helped it uphold its core values and what benefits it has effectively offered to them. - Strategic Channel Selection:
Selecting social media, TV, print, or digital platforms through which the message can be amplified makes the effectiveness of advertising more profound. Maximum reach and impact will then enable that brand to top the consumer’s mind.
Brand awareness builds a foundation for future interactions. Familiarity is of the essence in a competitive marketplace.
2. Persuasion and Influence

Persuasion and influence are intrinsic to advertising. It’s constructed to not only inform but influence the attitudes of, and eventually the behaviour of, the target consumers. There are three primary characteristics of that function:
- Emotional Appeals:
Appeals that create a sense of happiness, nostalgia, or sympathy make the consumer develop a stronger bond between the consumer and the appeal. For example, an advertisement where a family enjoys their food as a family can be felt in the warmth it evolves and then the consumer associates the latter with the brand. - USPs – Clear Difference Communication in Advertisements:
Advertisers must clearly communicate in their ads what differentiates the offering from a competitor in terms of quality, newness, and service. Comparative advertising has its own value if done judiciously. - Validation by Testimonials:
Testimonials, endorsements, and user-generated pieces of evidence are powerful tools with which a brand’s claims are validated. It gives credence, makes it attractive, and influences the consumer’s way of thinking about the offering.
Advertising functions therefore include persuasion and influence as it acts to shape consumers’ views of the brands and their offerings.
3. Production of Sales and Revenue

The very point of advertising is to create sales and revenue. In this respect, three points summarize the above function:
- Creating Urgency:
Terms like “limited-time offer” or “exclusive discounts” appeal to the customer’s fear of missing out. This strategy is most effective, though, during promotions and seasonal sales. - Long-Term Brand Loyalty:
A good advertisement campaign can definitely increase direct sales, but it can also help in long-term brand loyalty and repeat purchases. Continuous messages, quality goods, and concern for customer satisfaction may lead to sustained business growth. - Measuring Success:
Through the use of metrics like return on investment (ROI) and customer lifetime value (CLV), brands can determine how successful their advertising has been, depending on the sales and revenues it yielded. This also means that in future strategies, those metrics and values could be utilised to alter and improve the advertising campaign.
General Purpose of Advertising:
The most obvious main purpose of advertising is to increase sales and revenue for a business. This is what keeps and expands a business.
4. Communication to the Target Markets
Communication with the target markets involves education through advertisement. While the primary job of advertising is to induce sales, educating the target group is another very important task. Here are three essential characteristics of educative advertising:
- Informative Messages:
Advertising can communicate valuable information to audiences for intelligent decision-making. This is especially helpful when new products are launched or complex offerings are involved.
Educational advertising does a lot of work in showing why a product should be bought based on its features and benefits. For example, a technology company can have its ads demonstrate how to use a new gadget while highlighting unique functionalities and ease of use. - Positioning as a Subject Matter Expert:
Helpful content—tutorials, guides, or explainer videos—boosts the trustworthiness and credibility of a brand with the target audience. That is to say, it will not only educate them but also empower their reputation virtually.
Educational advertising and consumer decision-making
Educational advertising often results in an empowered consumer decision and thus enriches the experience of a customer.
5. Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty is the foundation upon which long-term business success is built, and advertising can be critical in developing it. Here are three points on customer loyalty through advertising:
- Loyalty Programs:
Advertising schemes for loyalty programs such as points-based schemes, exclusive discounts, or pre-sale access to sales increase repeated purchases and, in turn, customer retention. These schemes give a feeling of belonging. - Consistent Messaging:
Customers are bound to love the brand because consistency on all channels begets loyalty. When a customer sees an ad that speaks to his belief system and his very life, he is likely to identify with the brand. - Creating Advocates:
After some time, the emotional attachment will culminate into loyalty, and happy customers become advocates for a brand, referring other people by word of mouth. This organic source of promotion can do wonders to extend the reach and credibility of a brand.
Emotional loyalty through advertising not only brings repeat business but also helps the consumer become a passionate advocate for the brand.
Final Thoughts
The functions of advertising are highly diverse. Each purpose has a very specific role that fits under marketing’s vast purview. Here are three final takeaways:
- Integral Marketing Strategy:
Understanding the diverse functions of advertising helps brands create integral marketing strategies that cater to consumers’ various needs. - Strategic Integration:
A firm’s message across all channels will be consistent with an effective marketing approach through the use of advertising functions. - Long-term Success:
Good advertising will communicate value, inspire trust, and will eventually have a brand that is more meaningful to the consumer in the long run.
Suppose the real core functions of advertising are understood and effectively applied. In that case, it is possible to handle the intricacies of consumer behaviour, increase brand presence, and cause long-run growth. Taking on board these functions of advertising will enable the brands to reach even better connections with the target audience, thus resulting in more success for themselves in the competitive marketplace.
]]>Importance and Relevance
- Advertising campaign planning is indispensable for brands that desire to benefit from their marketing efforts.
- A unique marketing campaign can be the difference between catching the consumers’ eye and becoming just another advertisement in a world where numerous commercials bomb consumers daily. And it can prove critical.
- In companies, proper planning of marketing campaigns can make a difference; through this, they can increase brand awareness, customer involvement, and, eventually, sales.
- Mastering the art of campaign planning is the key to successfully navigating the complexity of different marketing channels, whether traditional media or social platforms.
- Advertising campaign planning is the best way to get invaluable practical insights and knowledge on how to go about things if you are a marketer who wants to cover more ground in the market or a business leader who is planning to stir up your audience engagement.
Understanding Advertising Campaign Planning

- In advertising campaign planning, a systematic method involves creating a structured approach for promoting a product, service, or brand.
- This approach is a collection of things central to its purpose, such as being adequately structured, based on data, and supporting specific marketing goals.
The Importance of Defining Campaign Objectives
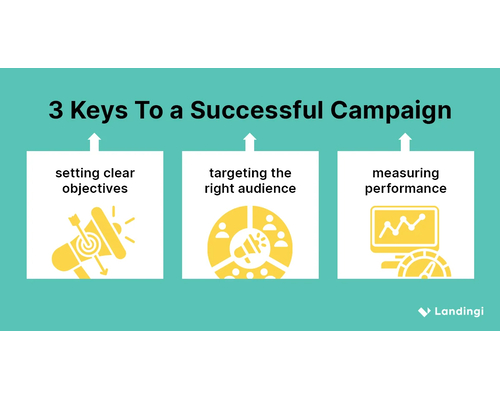
- The first, most vital, and most crucial process in advertising campaign planning is to identify clear and measurable objectives.
- This base is the one that everything else is founded on and being sure about what to do.
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound (SMART) Goals
- By applying the SMART structure, it is much easier to recognize the objectives of the marketing activity and thus make achieving those goals the campaign purpose.
- For example, instead of “increase sales,” a SMART goal will be “to achieve a sales growth of 20% in the subsequent quarter.” Detailed target varying facilitates keeping tabs on the process and estimating achievement at the end of the promotion.
Audience Targeting and Segmentation
- Comprehending the target audience is fundamental for a campaign to reach its objectives.
- The marketing research and data analyses reveal the demographic attributes, preferences, and behavior used for positioning or messaging.
- For example, campaigns directed at Gen Z and baby boomers will diverge immensely. It is indicated that by tailoring the campaigns to the audience’s taste, there is up to 50% more engagement.
Frameworks for Successful Campaigns
- Models such as AIDA (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action) give a shopper’s journey graphic for each stage of the campaign, thus fulfilling potential buyers’ specific needs and emotional aspects.
- Implementing a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is another method to strengthen strategy and execution.
Crafting the Right Message and Channel Strategy
- Once the goals have been set, the following action is to create the right message and select the suitable communication channels for its delivery.
Message Development and Positioning
- To be relatable, the messaging should reflect the audience’s values and preferences.
- One good example is Nike’s and Apple’s ability to touch the hearts of their customers through their slogans and branding narrations.
- Differentiation of messages is a requirement in the marketplace as spectators; hence, you will have to give a good reason for consumers to turn to the brand instead of competitors.
Multi-Channel Approach
- Modern advertising systems are growing because of the diversity they are enforced with. Usually, a multi-channel strategy will be the best approach to achieve the desired results.
- Brands can use social media, email, television, and offline marketing methods to give customers consistent messages and remember.
- The collaboration of a social media campaign with influencer partners can not only expand the reach but also increase engagement.
Challenges and Considerations
- Every campaign entails several risks, such as budget deficiencies and limitations prescribed by particular channels.
- Effective planning implies the necessity of being adaptable, i.e., adjusting the tactics according to real-time data and customer feedback.
- Moreover, respecting the law and ethical considerations, such as data protection laws, should be the basis for maintaining the brand’s validity and trust.
Measuring Success and Making Adjustments
- The last action of the advertising campaign is measurement and analytical review, which are the most important when explaining the positive and negative messages.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Identifying and tracking KPIs is crucial to the evaluation of the effectiveness of a campaign.
- The common ones are return on investment (ROI), click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and the total size of the audience that the promotional campaign reaches. By using these indicators, businesses can understand the outcomes of their advertisements.
Iterative Learning and Adjustments
- Considering the insights obtained by data, the direction of iterative learning requests brands to re-evaluate whether their choices provide more or less customer satisfaction.
- They can exploit the successes/inefficiencies in their campaign and reduce future brand electrolytes.
- A practical example of this would be knowing that the ad format led to more engagement, so to be the step to be followed, it should be significantly controlled for the wrong cases.
Emerging Trends in Advertising

- Keeрing an eye on contemporary moves in advertising, like the spreading use of artificial intelligence in data analysis or the video content trend, will give branding a competitive edge.
- Moreover, incumbents are faced with the dilemma of staying abreast of the constant changes in the market. Besides that, improving strategies to capture underserved customers is also an ever-lurking challenge.
- In a nutshell, a good advertising campaign is planned to let the companies reach their goals strategically, designing their messages for each platform that they either communicate their plan with or trying to be consistent with their approach to measuring metrics.
Conclusion
- Advertising campaign planning is the most crucial step in advertising, and it determines the differentiating factors between successful marketing endeavors and brand awareness.
- Through the specific means of presenting a business that does its work well and the company that is engaged in the advertiser creative, which both employees and consumers can understand, the advertiser will eventually attract more customers. This can be done through careful financial planning, ensuring customer loyalty, and brand enhancement.
- The elements of advertising campaign planning, such as research, strategic development, carrying it out, and assessment, create parties that drive involvement and accomplish the proper effectiveness when performing with one another.
- A systematic arrangement of the planning process ensures the alignment of all the components with the overall company objectives, consequently developing a lean process from origin to implementation.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic Objectives: The campaign’s clearly defined aims help focus its direction and measure its success.
- Target Audience: Knowing who your customers are makes the message more applicable and impactful (Try to remove this line).
- Channel Selection: Picking the most effective distribution platforms to spread the word gives us colossal brand visibility and engagement psychometrics that help determine how the cost should be spent.
- Creative Messaging: Impressive content holds the audience, encouraging them to purchase.
- Budget Management: A promising strategy allows resources to be used for their intended purpose.
- Performance Evaluation: Continuous monitoring allows us to modify them correctly and keep them effective for longer.
To produce comprehensive advertising campaigns pertinently and for the final objectives to surpass their plans, businesses need to prioritize each of them accordingly. Recognizing that successful campaign planning will lead to a higher degree of competitiveness in a world of varying priorities is key.
]]>Nike marketing campaigns are about much more than selling stuff; they encapsulate the brand’s ethos and inspire millions to stretch limits. The following are key points concerning Nike’s successful marketing strategies:
- Emotional Association: The company appeals to a customer’s emotions.
- Innovations at its Core: It also underscores innovation through its products, advertising, and promotional activities.
- Inspiring Sportsmen: The company’s campaign most often involves sportsmen overcoming barriers to inspire consumers.
- Target audience is varied: Nike appeals to every section of society.
- Innovative Use of Technology: Nike engages and interacts with people through its innovative technologies.
Among the top marketing strategies in the major is Nike. This company is also an example in the present and future, as people look to endorse innovative ways. Connecting individuals deeply in an emotional perspective using recognized phrases such as “Just Do It” is just enough for Nike’s foothold in the marketplace.
What is Nike?

Nike, Inc., is an American multinational company founded in 1964. The company specializes in designing and manufacturing shoes, sportswear, and gear and sells them worldwide. It is currently the world’s largest manufacturer of shoes and apparel, establishing quality and innovation as the benchmark.
Key Features of Nike
- Product Line: The company offers various products, from running shoes to casual wear, sportswear, and accessories.
- With technological and design innovations, Nike ensures its products meet the diverse needs of athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
- Global Reach: Nike sells its products in over 190 countries, making it a brand name. This broad reach enables Nike to hold its position in the market while increasing its customer base.
- Brand Image: Nike is a brand name associated with quality athletic equipment and has been at the forefront of sportswear innovation. It has created a great brand image through decades of effective marketing and quality products.
- Innovative Products: Nike continues to fund research and development to produce cutting-edge athletic gear, which positions the company alongside other rivals in this fast-changing market.
- Cultural Impact: Nike has become a symbol of culture, with its influence cutting across fashion, sports, and lifestyle. The brand’s participation in different movements made it stick around beyond just being sportswear.
In a nutshell, Nike is above any brand: it is a global phenomenon that embodies aspiration, performance, and innovation.
Why Nike Markets?

Nike’s primary marketing strategy is to emotionally connect with customers and establish itself as the market leader in sports equipment. This becomes the foundation for sales and encourages a fit lifestyle.
Why Nike Hones Its Focus on Marketing
- Emotional Appeal: Nike’s marketing is highly based on personal stories and aspirations. By relating to consumers emotionally, Nike creates loyalty and trust.
- Brand Leadership: The goal is to be the first brand that strikes one’s mind when thinking about athletic gear. By consistently portraying itself as a leader, the brand gains authority in the market.
- Inspiration: Nike inspires people to follow their passions and lead active lives. The company has athletes with some kind of barrier, which the public can easily associate with.
- Targeted Communication: Nike develops communications designed to reach a particular group of people. The company can market its products correctly by knowing its consumers’ diverse needs.
- The adoption of new technologies allows Nike to interact more with its customers. Nike connects to its consumers through technology such as social media campaigns and interactive experiences.
In short, Nike’s marketing philosophy revolves around creating a story through which the consumer identifies at an extremely deep level so that he becomes a part of the brand’s journey.
Best Nike Marketing Campaigns
Nike’s marketing campaigns are just a legend. Creativity and motivational, solid, and empowering messages blend. Here are eight campaigns that symbolize the excellence of Nike in marketing:
Just Do It

- Launched in: 1988
- Impact: The slogan encouraged people to break barriers and overcome difficulties and became a general appeal.
- Media Used: The print and outdoor ads covered the broadest range of consumers.
- Emotional Association: It built a tremendous emotional association for consumers with Nike.
- Cultural Relevance: Over the years, “Just Do It” has grown from a marketing phrase to an inspirational one that rouses millions.
The Last Shot

- Campaign Summary: It was launched in 2002 and featured basketball icon Michael Jordan. It focused on the last shot in a game.
- Message: A message of perseverance and never giving up resonated with athletes and sports lovers.
- Visual Attraction: The campaign brought out sports drama and excitement, enhancing its appeal.
- Brand Inspiration: It positioned Nike as an inspirational figure in the athletic community, further consolidating its market dominance.
- Emotional Resonance: It focused on a pivotal moment in sports, which connected it with the audience on a deep level, making them feel part of the action.
Find Your Greatness

- Essence: It was more about Nike’s sportswear—something to improve people’s abilities in it.
- Inspiration content: Video clips depicting how various athletes went beyond one hurdle after another appeared within the message.
- Target Audience: The advertising addressed an extensive range of strict athletes to enthusiastic exercisers.
- Media Used: Print and outdoors, in addition to all new online media, with this mass-reach opportunity, there ended the full set.
- Cultural Influence: It pushed people into sports and exercise by making greatness within anyone’s reach.
Breaking2

- Overview: “Breaking2” is one of the most innovative ideas ever, as it tried to break the barrier of two hours set up for a marathon.
- Novelty Approach: This combination of two diverse entities, sports, and technology, displays Nike’s willingness to be innovative.
- Live Show: Its primary focus is holding the live show where leading runners try to break the record and capture everyone’s attention worldwide.
- Engagement: Nike involved people in history; that way, it made them form community and excitement.
- Marketing Strategy: The campaign proved Nike’s creative intent; there was a sense of ambition about the limits of sporting performance.
Dream Crazy

- Overview: “Dream Crazy” was a powerful commercial by Nike featuring a dramatic short film with athletes overcoming challenge after challenge.
- Message of Ambition: It provoked ambition in viewers to have the dream regardless of all odds.
- Celebrity Endorsement: It consisted of sportspersons, thus making the advertisement more real and extensive.
- Cultural Relevance: The advertisement was relevant to customers as it represented the issues of society and their struggle for social causes.
- Brand Fit: This advertisement aptly reflected Nike’s vision, thereby increasing its credibility as a brand that promotes ambition and toughness.
Bo Knows

- Campaign Idea: The “Bo Knows” advertisement with NFL and MLB sportsman Bo Jackson perfectly combines comedy and sporting brilliance.
- Cross-Cultural Appeal: It showcased Jackson’s sportiveness across diverse sports and became a sight to the giant crowds.
- Celebrity Pull Factor: The ad campaign used the celebrity factor tagged along with Jackson to enhance brand visibility and product sales.
- Humor Innovation: The humor-based approach made the campaign memorable and amplified engagement value.
- Long-Term Contribution: It is the most classic instance of Celebrity Endorsement in any advertisement campaign.
Nike Women

- Synopsis: “Nike Women” promoted women’s athletic wear and assisted in giving women athletes the force for empowerment.
- Celebration of Women: It reflected the best performances of women athletes, thus speaking directly to the women consumer’s heart.
- Inspirational Messaging: This campaign had excellent imagery and storytelling that inspired women to work for their athletic pursuits.
- Market Positioning: This campaign communicated Nike’s commitment to diversity and inclusion in sports.
- Brand Loyalty: The theme of empowerment among women created much loyalty in female consumers.
Nike ID

- Campaign Overview: The Nike ID changed the way consumers of sports apparel could engage with the brand’s product.
- Personalization: This campaign allowed customers to act out their individuality when they chose personalized shoes and sportswear.
- Interactive Experience: An online, accessible interface enhances customer engagement with the brand.
- Brand Love: The possibility of tailoring strengthened consumers’ emotional attachment to the brand.
- Market Impact: This innovative approach increased brand awareness and sales, indicating the power of personalization in marketing.
Conclusion
Nike shines through a comprehensive and innovative advertising strategy in a market total of with a brandwidth company’s ability to inspire and engage its audience emotionally makes it a leading name in the sports apparel industry. By creating relatable stories, leveraging technology, and positioning itself as a symbol of empowerment, Nike has carved out a niche that resonates with diverse consumers.
Final Thoughts
- Emotional Marketing: Nike successfully taps into consumers’ emotions, creating connections beyond the initial purchase.
- Innovative Strategies: Using cutting-edge marketing strategies keeps the brand fresh and relevant.
- Cultural Impact: Nike’s influence extends beyond sportswear, making it a cultural icon.
- Diversity: The brand targets a broad audience, from elite athletes to fitness enthusiasts.
- Community Building: Through its campaigns, Nike fosters a sense of community among its consumers, reinforcing brand loyalty.
Nike has become more than just a brand; it is a movement that encourages people to dream big and push their limits.
]]>Ready to talk with a marketing expert?
Get in Touch
Rukmini Knowledge Park, Kattigenahalli, SH 104, Srinivasa Nagar, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560064
+91-990 247 8800
contact@gingermediagroup.com
Popular in Television Advertising
Udaya TV AdvertisingSun TV AdvertisingStar Plus AdvertisingTV 9 AdvertisingZee TV AdvertisingNDTV India AdvertisingColors TV AdvertisingPopular in Airport Advertising
Spice Jet AdvertisingMumbai Airport AdvertisingDelhi Airport AdvertisingEmirites AdvertisingIndiGo Airlines Domestic India AdvertisingPopular in Newspaper Advertising
Deccan Herald AdvertisingPrajavani AdvertisingThe Hindu AdvertisingEconomic Times AdvertisingDainik Jagran AdvertisingHindustan Times AdvertisingPopular in Magazine Advertising
Forbes AdvertisingCosmopolitan AdvertisingBusiness World AdvertisingVogue Magazine AdvertisingPopular in Sports Advertising
IPL AdvertisingPopular in Outdoor Advertising
Billboard AdvertisingBus Shelter AdvertisingMetro Pillar AdvertisingUnipole Advertising© Ginger Media Group 2025. All Rights Reserved.
