RACE, an absolutely essential tool these days, helps to improvise business processes, boost engagement, and optimize marketing strategies. The full form of RACE is Reach, Act, Convert, and Engage. The RACE framework has been designed as an effective strategic model to enable a business to design a perfect customer journey, thereby enhancing the overall marketing performance of that business. In this blog, we talk about the basics of RACE and its constituent elements that provide a road to success in any modern organization.
- Reach: The first step included in the journey of the customer. It attracts potential customers.
- Act: It helps create an interaction with the brand, such as website visits and social media engagements.
- Convert: At this conversion stage, leads become paying customers.
- Engage Long-term relationships with the customer for higher loyalty and repeat purchases.
- RACE Strategy: Integrated Strategy in Optimizing the Leverage of Marketing Channels Efficiency and Returns on Investments.
What is RACE?
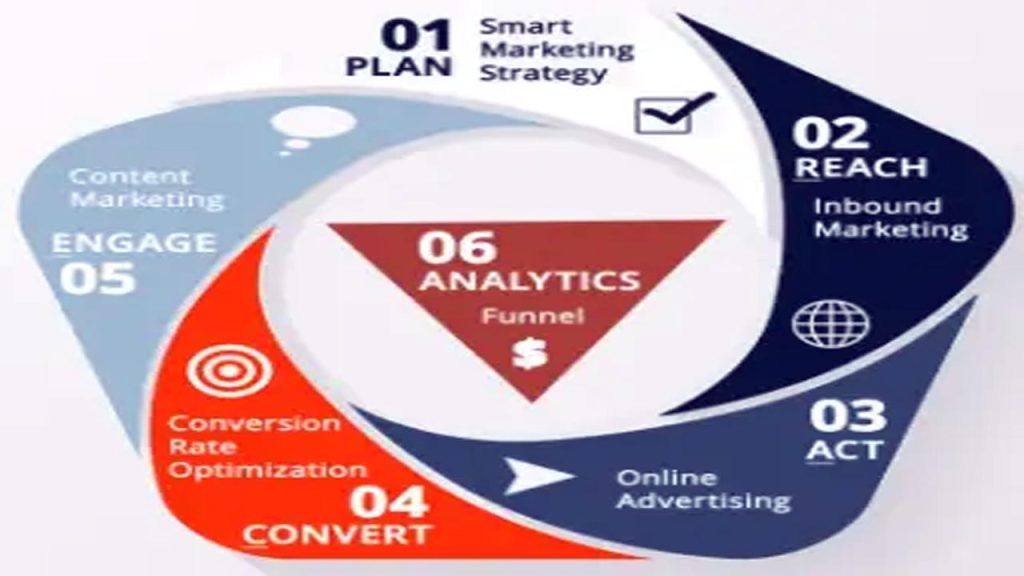
RACE is a strategic framework organizations use to leverage a structured process for digital engagement while enhancing marketing performance. By understanding the four levels: Reach, Act, Convert, and Engage, businesses can optimize the process for customers, improve conversion rates, and deepen brand loyalty. Every phase in the RACE cycle presents opportunities for improvement in an organization’s approach to marketing.
Important Elements of RACE:
- Reach: The process through digital channels like social media, SEO content marketing to attract potential customers.
- It is the most critical stage as this is when brand awareness and interest are created, and you get in front of the right audience.
- Act: It involves encouraging customers to interact with your brand, such as visiting your website or sharing a post on social media.
- Building trust at this level makes the user want to interact with your brand while building a connection with the right customers.
- Convert: It transforms an engaged user into a paying customer.
- This stage guides leads into the sales funnel, converting them into potential buyers via well-optimized processes.
- Engage: Creating long-term relations with customers after a sale.
- Keeping customers interested in a product after their purchase triggers repeat business and loyalty, leading to continuous business growth.
Advantages of RACE
The RACE framework provides various benefits to modern organizations as it covers a major part of the customer journey. Using this structured process, businesses can ensure that their marketing strategies are optimized in terms of both performance and customer satisfaction.
- Better Decisions: The insights achieved through each of the RACE process stages will allow businesses to make more informed decisions in consistency with their objectives.
- Analysis of engagement data leads firms to bestow upon their company new strategies according to what works and what does not with the target.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By focusing on those activities that provide maximum ROI, there is better resource allocation.
- The unnecessary expenses are curbed here so that ample attention is given to concentrate efforts toward giving maximum multiplier effect in marketing practices.
- Customers First Approach: The need is put across at the forefront of customer needs; hence, the firm attends to this factor and reacts accordingly based on the sentiments of the audience.
- Customer-centric inspires customers to be loyal and be involved in more brand work.
- Continuous Improvement: RACE emphasizes the continuous review of marketing activities to ensure continuous growth and optimization.
- Businesses can keep themselves at the competition bar by aligning their actions according to performance metrics.
- Collaboration and Communication: The RACE model encourages teamwork to ensure that every department aligns itself with the business objective.
- Well-defined goals and identified roles within this framework ensure transparency and effective communication.
Steps to Implement RACE
Businesses should execute business with an orchestrated approach that combines key strategies and performance metrics for proper operation of the RACE framework. This improves the optimization process in the customer journey and enhances business results.
- Examine Current Activities: Look at what is currently being marketed to identify the firm’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Gaps in customer journeys will determine where to create emphasis on the best-performing business strategy.
- Design Cost Drivers: What is driving cost at every stage of the RACE model.
- Efficiency would rise since resource allocation and distribution will be known.
- Develop Performance Measures: Track engagement and conversion at every stage of the framework to measure success.
- Data-driven insights will empower businesses to make appropriate adjustments.
- Employee Engagement: Engage all departments in the process of implementation. This brings a sense of ownership and responsibility to the employees.
- When active, staff play their role in executing the marketing plan in the right manner.
- Utilize Technology: Make use of CRM systems and marketing automation to facilitate smooth operation and monitor the progress.
- It enhances the efficiency of RACE and also enables businesses to scale their efforts correspondingly.
Real-Life Implementations of RACE
This framework proved to be effective in any industry to enhance the performance of any marketing undertaking as well as the relationship between the organization and the customers. The following is a number of success examples of applying the RACE model by businesses.
- Retail: A leading eCommerce retailer applied the RACE framework for the purpose of raising customer engagement, mainly on the stage of Convert. By optimizing the checkout process, the company saw an increase in conversion by 25%.
- Consumer Goods: The global consumer goods brand applied RACE to enhance its Reach Strategy; indeed, the outcome was a significant spike in the presence of the brand and customer acquisition through targeted campaigns.
- Software: A software firm implemented the Engage phase with a loyalty program, raising the rate of return by 40% while enhancing advocacy among the satisfied users.
- Healthcare: Hospitals introduced the use of RACE in the promotion of patient engagement, particularly through online outreach programs, which has helped make booking an appointment and after-care follow-ups easier and more efficient for the hospital.
- Hospitality: Hotels have utilized the Engage stage to create long-term customer relations through tailored offers and loyalty plans that have helped in consumer retention.
Final Thoughts
The RACE framework hence works as a very powerful tool for businesses to enhance their marketing efficiency, strengthen interactions with customers, and perfect their entire customer journey. Businesses can now, through these individual steps of the campaign-to-marketing funnel: Reach, Act, Convert, and Engage, gain scope for growth, increase customer satisfaction, and ultimately make profits.
- Employee Engagement: RACE implementation thus helps in constructing a sense of belonging and gives impetus to teams, thereby enhancing performance.
- Better Decision Making: Decisions made in real-time are data-based, so there is always a marketing approach that works.
- Increased ROI: Proper usage of all the stages increases the return on investments.
- Customer Loyalty: Engaging customers beyond the point of purchasing something more results in an enhanced, strong relationship that makes them brand advocates.
- Sustainable Growth: Continued assessment and optimization of marketing efforts will eventually lead to long-term success.
Now is the time to embrace the RACE framework and experience the transformative impact it can have on your organization. As already known, to be competitive enough in today’s market, businesses focus on improving customer interactions with them and maintaining sustainability, ensuring sustainable growth.
]]>- Strategic Communication: Advertising is not about conveying a message but rather creating a story that gives the user power.
- Emotional Engagement: Advertising alone can be an effective device for emotional engagement between a brand and a consumer.
- Long-term Impact: Advertising is not about short-term sales; it is a vehicle for building brand identity and loyalty over the long haul.
As we examine this topic, it becomes clear that advertising goes beyond a message; it is a multidimensional approach designed to communicate value and create lasting ties.
Functions of Advertising
1. Building Brand Awareness

Brand awareness is always at the root of a successful marketing plan. Without that, even the greatest products and services can remain in obscurity. It is through advertising that a brand becomes visible and therefore acknowledged by its target audience. Here are three must points regarding brand awareness:
- Target Audience Identification:
Identification of the target group based on demography, interests, and behaviour is equally significant. To achieve this, detailed market research, surveys, and data analysis about the consumer are essential. Using tools like Google Analytics and insights from social media, brands can obtain valuable information related to customers’ preferences and online behaviour. - Compelling Messaging:
A compelling message that communicates with the audience must be created once the target audience is defined. It needs to indicate how the USPs of the brand have helped it uphold its core values and what benefits it has effectively offered to them. - Strategic Channel Selection:
Selecting social media, TV, print, or digital platforms through which the message can be amplified makes the effectiveness of advertising more profound. Maximum reach and impact will then enable that brand to top the consumer’s mind.
Brand awareness builds a foundation for future interactions. Familiarity is of the essence in a competitive marketplace.
2. Persuasion and Influence

Persuasion and influence are intrinsic to advertising. It’s constructed to not only inform but influence the attitudes of, and eventually the behaviour of, the target consumers. There are three primary characteristics of that function:
- Emotional Appeals:
Appeals that create a sense of happiness, nostalgia, or sympathy make the consumer develop a stronger bond between the consumer and the appeal. For example, an advertisement where a family enjoys their food as a family can be felt in the warmth it evolves and then the consumer associates the latter with the brand. - USPs – Clear Difference Communication in Advertisements:
Advertisers must clearly communicate in their ads what differentiates the offering from a competitor in terms of quality, newness, and service. Comparative advertising has its own value if done judiciously. - Validation by Testimonials:
Testimonials, endorsements, and user-generated pieces of evidence are powerful tools with which a brand’s claims are validated. It gives credence, makes it attractive, and influences the consumer’s way of thinking about the offering.
Advertising functions therefore include persuasion and influence as it acts to shape consumers’ views of the brands and their offerings.
3. Production of Sales and Revenue

The very point of advertising is to create sales and revenue. In this respect, three points summarize the above function:
- Creating Urgency:
Terms like “limited-time offer” or “exclusive discounts” appeal to the customer’s fear of missing out. This strategy is most effective, though, during promotions and seasonal sales. - Long-Term Brand Loyalty:
A good advertisement campaign can definitely increase direct sales, but it can also help in long-term brand loyalty and repeat purchases. Continuous messages, quality goods, and concern for customer satisfaction may lead to sustained business growth. - Measuring Success:
Through the use of metrics like return on investment (ROI) and customer lifetime value (CLV), brands can determine how successful their advertising has been, depending on the sales and revenues it yielded. This also means that in future strategies, those metrics and values could be utilised to alter and improve the advertising campaign.
General Purpose of Advertising:
The most obvious main purpose of advertising is to increase sales and revenue for a business. This is what keeps and expands a business.
4. Communication to the Target Markets
Communication with the target markets involves education through advertisement. While the primary job of advertising is to induce sales, educating the target group is another very important task. Here are three essential characteristics of educative advertising:
- Informative Messages:
Advertising can communicate valuable information to audiences for intelligent decision-making. This is especially helpful when new products are launched or complex offerings are involved.
Educational advertising does a lot of work in showing why a product should be bought based on its features and benefits. For example, a technology company can have its ads demonstrate how to use a new gadget while highlighting unique functionalities and ease of use. - Positioning as a Subject Matter Expert:
Helpful content—tutorials, guides, or explainer videos—boosts the trustworthiness and credibility of a brand with the target audience. That is to say, it will not only educate them but also empower their reputation virtually.
Educational advertising and consumer decision-making
Educational advertising often results in an empowered consumer decision and thus enriches the experience of a customer.
5. Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty is the foundation upon which long-term business success is built, and advertising can be critical in developing it. Here are three points on customer loyalty through advertising:
- Loyalty Programs:
Advertising schemes for loyalty programs such as points-based schemes, exclusive discounts, or pre-sale access to sales increase repeated purchases and, in turn, customer retention. These schemes give a feeling of belonging. - Consistent Messaging:
Customers are bound to love the brand because consistency on all channels begets loyalty. When a customer sees an ad that speaks to his belief system and his very life, he is likely to identify with the brand. - Creating Advocates:
After some time, the emotional attachment will culminate into loyalty, and happy customers become advocates for a brand, referring other people by word of mouth. This organic source of promotion can do wonders to extend the reach and credibility of a brand.
Emotional loyalty through advertising not only brings repeat business but also helps the consumer become a passionate advocate for the brand.
Final Thoughts
The functions of advertising are highly diverse. Each purpose has a very specific role that fits under marketing’s vast purview. Here are three final takeaways:
- Integral Marketing Strategy:
Understanding the diverse functions of advertising helps brands create integral marketing strategies that cater to consumers’ various needs. - Strategic Integration:
A firm’s message across all channels will be consistent with an effective marketing approach through the use of advertising functions. - Long-term Success:
Good advertising will communicate value, inspire trust, and will eventually have a brand that is more meaningful to the consumer in the long run.
Suppose the real core functions of advertising are understood and effectively applied. In that case, it is possible to handle the intricacies of consumer behaviour, increase brand presence, and cause long-run growth. Taking on board these functions of advertising will enable the brands to reach even better connections with the target audience, thus resulting in more success for themselves in the competitive marketplace.
]]>Psychological Pricing
Psychological pricing uses people’s perception of numbers. According to researchers, people process prices starting from the leftmost digit and usually ignore the rightmost digits. As such, it gives the illusion that prices are cheaper than they are. Many businesses apply this pricing technique as a means of intensifying competitive advantage. The ultimate objective of psychological pricing is to meet the consumers’ psychological needs and make them believe they are saving a lot.
Some of the major examples under psychological pricing include:

- Playing with Prices: At the time of retailing, the commodities are priced at Rs 999 rather than Rs 1000. This will appear cheaper, and the customers will believe they are spending many more rupees than they do.
- Comparative Advantage: A “50% off” sale is mathematically identical to “Buy One, Get One Free,” but customers generally prefer the latter—it just seems like a better deal.
- Time-Limited Offers: Creating perceived scarcity by proclaiming, “Hurry, only a few hours left!” forces customers to speed up purchases.
- Pricing with Rounding: For instance, pricing at Rs 99.99 instead of Rs 100 creates an illusion regarding the pricing, although the difference is merely marginal.
- Bundle Deals: Price offers like “3 for Rs 99” create an impression in the customer’s mind that he or she is getting a deal when, in fact, he or she isn’t because the per-unit price may be equivalent to the regular price.

Benefits of Psychological Pricing
Psychological pricing allows businesses to offer several benefits, especially in achieving more sales and revenues as well as maximizing profit. One advantage is that it creates a perception of value and pushes customers to make a decision faster.
Some of the major advantages are as follows:
Lower Price Band Perception

- Expensive products can be made to appear better valued if priced in a more affordable price band. For example, a Rs 39,999 product will appear as Rs 30,000 when, in fact, it is almost Rs 40,000.
More Return on Investment

- With the help of psychological pricing, companies can increase sales. Whenever consumers feel that they are getting a good bargain, they like the idea of getting one and buying one in order to increase the overall return on investment.
Customer Engagement

- If it is a food chain or shop, psychological pricing engages the customers through discounts given to customers and makes them feel that they should not miss their offers.
Customer Loyalty
- Low prices influence loyal customers. Psychology makes the customer come back to the brand, offering value.

Value Perception:
- Psychological pricing makes the product look cheap even though its actual price difference is not significant. This makes the product look like a better value.

Disadvantages of Psychological Pricing
While psychological pricing has many benefits, it must be remembered that it also has disadvantages. Some companies use this strategy excessively, thereby damaging their brand image or creating false expectations of their products.
The main disadvantages are as follows:
Create Long-Term Pricing Expectations

- While psychological pricing has many benefits, it must be remembered that it also has disadvantages. Some companies use this strategy excessively, thereby damaging their brand image or creating false expectations of their products.
Customer Unsatisfaction

- Besides psychological pricing, the hidden costs will make the customer feel deceived and unsatisfied.
Loss of More Customers

- If all firms employ similar tactics, the customers become skeptical. They feel they are being manipulated, or the real price is not presented, and they need to switch to the competitor’s product.
Sales Are Not Guaranteed
- The theory, as such, does not state that the consumers will buy more because it is sold cheaper. If they believe the product is of a lower quality, they will not buy it.
Not Extremely Effective
- Sometimes, people also do not pay much attention to small differences in prices. Thus, psychological pricing is not all that effective after all. A product tagged at Rs 99.99 is still considered to be priced at Rs 100.
Common Psychological Pricing Devices
Many psychological pricing techniques are used to give the consumer a sense of urgency, value, or scarcity to make him act in an accelerated decision-making process. The most common techniques include the following:
- Charm Pricing: Prices end at .99 or .95. That makes the price seem cheaper than it is. For example, Rs 999 sounds more attractive than Rs 1000 because the difference is only one rupee.
- Bundle Pricing: It is a promotional device through which some items are sold at one price (e.g., “3 for Rs 99”). Consumers feel they are getting a deal while the per-item price is the same as it would have been if they had purchased each item separately.
- Price Anchoring: The actual price is laid alongside the discounting price in a shop. That way, the discount would look larger. The product was originally Rs 2000, and it now retails for Rs 999; that is a huge bargain.
- Time Limits: Flash sales or “limited-time” discounts make customers purchase on impulse because they would have felt deprived had they not made the required purchases.
- Loss Leader Pricing: Selling a product at a loss to attract customers into a store or onto a website to buy higher-margin items.
How Psychological Pricing Influences Consumer Behavior
Psychological pricing influences consumer perception of value and the decision to buy. Businesses can make their product more attractive by appealing to the emotional response of the customer rather than lowering the price.
Psychological pricing consequently affects the behavior of the consumers as follows:
- Creation of Value Perceived: A consumer will believe he is getting a fantastic deal when they pay Rs 999, while in reality, it is but a pittance above Rs 1000.
- Inducement to Impulse Buying: Time-limited offers and discounting also stimulate impulse buying. Customers are subjected to the vagaries of urgent decision-making without overthinking.
- Avoidance of Price Resistance: With charm pricing, the business will not face price resistance from the customers. For instance, Rs 99.99 sounds psychologically far different from Rs 100, although the difference is indeed very minor.
- Customer Satisfaction: Consumers feel pleased and satisfied with their purchase decisions when they are convinced to get a bargain.
- Price Anchoring Effect: Placing the comparative price next to the actual price of offering a discount makes the discount look very high, therefore providing better value in the perception of a customer.
Final Thoughts
Psychological pricing can powerfully influence consumer behavior and, therefore, drive sales. Knowing how consumers read numbers allows businesses to strategically set prices with the aim of making these products more appealing to customers, i.e., less expensive. On the other hand, psychological pricing can be in balance with transparency to avoid losing customers because of distrust. Proper use of psychological pricing can increase the perceived value of products and services, driving sales simply by attracting more customers; it can further ensure customer loyalty through appealing price quotes.
- Drive impulse buying with scarcity-based offers.
- Offset small, almost insignificant changes in price that reap significantly higher profits.
Applying psychological pricing may be thought to be weird, but it truly is an effective marketing tool if applied carefully and strategically. From the utilization of consumer psychology, the opportunity for businesses to tweak prices with optimization in sales increases, which eventually leads to a better brand perception.
]]>Ready to talk with a marketing expert?
Get in Touch
Rukmini Knowledge Park, Kattigenahalli, SH 104, Srinivasa Nagar, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560064
+91-990 247 8800
contact@gingermediagroup.com
Popular in Television Advertising
Udaya TV AdvertisingSun TV AdvertisingStar Plus AdvertisingTV 9 AdvertisingZee TV AdvertisingNDTV India AdvertisingColors TV AdvertisingPopular in Airport Advertising
Spice Jet AdvertisingMumbai Airport AdvertisingDelhi Airport AdvertisingEmirites AdvertisingIndiGo Airlines Domestic India AdvertisingPopular in Newspaper Advertising
Deccan Herald AdvertisingPrajavani AdvertisingThe Hindu AdvertisingEconomic Times AdvertisingDainik Jagran AdvertisingHindustan Times AdvertisingPopular in Magazine Advertising
Forbes AdvertisingCosmopolitan AdvertisingBusiness World AdvertisingVogue Magazine AdvertisingPopular in Sports Advertising
IPL AdvertisingPopular in Outdoor Advertising
Billboard AdvertisingBus Shelter AdvertisingMetro Pillar AdvertisingUnipole Advertising© Ginger Media Group 2025. All Rights Reserved.
